Therapy works. Research shows it improves mental health, changes brain structure, and offers lasting benefits. Here’s why therapy is effective:
- 75% of patients improve within 6 months of psychotherapy.
- Therapy reshapes the brain through neuroplasticity, enhancing emotional regulation and reducing symptoms.
- It’s as effective as medication for anxiety, depression, and OCD, but equips you with long-term coping tools.
- Brain imaging studies confirm therapies like CBT and DBT create measurable changes in brain function.
- Strong therapist-client relationships significantly improve outcomes.
If you’re considering therapy, options like CBT, DBT, or online platforms can make care accessible and effective. Therapy not only addresses mental health issues but also improves overall quality of life with lasting results.
Brain Science and Therapy Effects
Brain Scans Show Therapy Results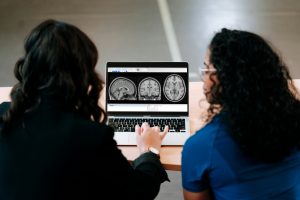
Brain imaging studies reveal that therapy can physically alter brain structure and function. For instance, research using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) found that Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) normalized brain activity in areas linked to panic disorder. Over 70% of patients undergoing CBT reached recovery, compared to just 7% in the control group. Similarly, Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) studies show that CBT repairs white matter connections in patients with OCD, which aligns with symptom improvement.
“Neuroplasticity is your brain’s ability to change. The structure of the brain can change physically to such an extent that it shows up on fMRI images. Because of documented proof of the relationship between Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and neuroplasticity, CBT is considered an evidence‑based therapy that works.” – Lukin Center for Psychotherapy
These findings highlight how therapy can reshape the brain, offering a foundation for understanding the unique effects of different therapeutic methods.
How Therapy Changes Brain Patterns
Various therapies lead to distinct changes in the brain. For example, a 2017 study on women with borderline personality disorder found that dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) increased grey matter volume in key brain regions. Here’s a breakdown of the changes:
| Brain Region | Change After Therapy | Associated Function |
|---|---|---|
| Anterior Cingulate Cortex | Increased grey matter volume | Emotional regulation |
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus | Increased grey matter volume | Behavioral control |
| Superior Temporal Gyrus | Increased grey matter volume | Processing social and emotional cues |
This data shows how specific therapies target particular brain areas, tailoring their impact to address unique challenges.
Therapy vs. Medication Effects
Therapy and medication improve mental health in different ways by affecting distinct neural pathways. Research shows that CBT strengthens connections within the brain’s executive control network, whereas medications typically create broader inhibitory effects across multiple networks. For example, a study on major depression treatments revealed that CBT uniquely enhanced cognitive control pathways. According to the researchers:
“The results revealed that the altered activation in the prefrontal cortex and precuneus were key regions related to the effects of CBT. Therefore, CBT may modulate the neural circuitry of emotion regulation. This finding provides recommendations for the rapidly developing literature.” – Shiting Yuan et al.
Therapy, unlike medication, results in long-term brain changes. By modifying gene expression and reinforcing neural connections, therapy offers lasting improvements in emotional and cognitive functions.
Treatment Types and Success Rates
CBT Success Rates and Studies
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has been shown to effectively treat various mental health conditions, often performing as well as or better than medication for issues like anxiety, depression, and OCD.
Here’s a closer look at what research reveals about CBT’s effectiveness:
| Condition | Treatment Success | Key Finding |
|---|---|---|
| Panic Disorder | Better than placebo | CBT combined with exposure therapy outperformed both no treatment and placebo controls |
| Social Anxiety | More effective | Delivered better outcomes compared to applied relaxation or waitlist control |
| Specific Phobias | Highly effective | In-vivo exposure therapy surpassed non-exposure methods |
“Overall, CBT appears to be both efficacious and effective in the treatment of anxiety disorders, but dismantling studies are needed to determine which specific treatment components lead to beneficial outcomes and which patients are most likely to benefit from these treatment components.” – Antonia N Kaczkurkin, PhD, University of Pennsylvania
In addition to CBT, newer therapies are showing promise.
New Therapy Methods: ACT and DBT
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) have gained traction as strong alternatives to traditional CBT. In a study of 177 inpatients, both ACT and CBT significantly reduced symptoms, with more than half of participants recovering from depressive symptoms.
DBT, in particular, has demonstrated notable results:
- A 75% remission rate for older adults when combined with medication, compared to just 31% with medication alone at a 6-month follow-up.
- Marked improvements in emotion regulation and reduced substance use among women with borderline personality disorder.
Here’s a quick comparison of CBT and DBT:
| Aspect | CBT | DBT |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 5–20 sessions | 6 months to 1 year |
| Focus | Present-centered | Includes processing past trauma |
| Approach | Change-oriented | Balances acceptance and change |
| Goals | Specific objectives | Enhancing overall life quality |
Long-term Results and Prevention
Therapy can have lasting effects on mental health. CBT, for example, has been linked to relapse rates as low as 0%–14%. This enduring improvement is attributed to therapy’s ability to reshape brain structure and function, leading to long-term positive changes.
How Does Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Work?
sbb-itb-e6bfb1d
How Therapy Creates Change
Therapy’s ability to create meaningful change comes not just from its effects on the brain and specific treatments but also from the strength of the therapist-client relationship and the structure of the sessions.
Patient-Therapist Connection
Studies highlight that the bond between a client and therapist often plays a bigger role in achieving positive outcomes than the specific techniques used.
A solid therapeutic alliance can lead to real, measurable benefits:
| Outcome Measure | Impact of Strong Alliance |
|---|---|
| Treatment Adherence | Higher attendance and greater engagement in sessions |
| Risk Reduction | Clients are twice as likely to see clinical improvement |
| Outcome Variance | About 7% of therapy outcomes are linked to the alliance |
“Anyone who dispassionately looks at effect sizes can now say that the therapeutic relationship is as powerful, if not more powerful, than the particular treatment method a therapist is using.” – John C. Norcross, PhD, ABPP, chair of the APA task force
Universal vs. Method-Specific Elements
While different therapies rely on unique strategies, certain universal elements – like setting goals together, providing regular feedback, and being culturally aware – are critical. When these basics are missing, 20%–40% of clients tend to drop out of therapy.
| Core Element | Effect on Treatment |
|---|---|
| Collaborative Goal Setting | Keeps patients engaged and focused |
| Regular Feedback | Lowers dropout rates and improves outcomes |
| Cultural Responsiveness | Boosts effectiveness across diverse populations |
Session Frequency and Outcomes
Research shows that attending therapy more frequently can speed up recovery. For example, data from 21,488 counseling center clients and studies involving 2,634 patients with anxiety, depression, and personality disorders reveal:
- Twice-weekly sessions lead to an effect size increase of 0.45 compared to weekly sessions.
- Greater session frequency in the first three months is linked to faster recovery.
- Weekly sessions result in quicker improvements compared to bi-weekly or monthly meetings.
“Session frequency appears to be an impactful component in delivering more efficient psychotherapy, and it is important to consider in individual treatment planning, institutional policy, and future research.”
These findings emphasize that consistent, frequent sessions – especially at the start – help accelerate recovery. Many providers recommend beginning therapy with more frequent sessions to build momentum, then adjusting the schedule as progress is made.
Online Therapy Access
Research has shown that virtual therapy is just as effective as in-person sessions. A meta-analysis of 47 studies involving 3,564 participants found almost no difference in outcomes between video-delivered psychotherapy (VDP) and traditional face-to-face therapy. This supports the idea that virtual therapy can provide effective care while being more accessible.
Televero Health Services
Televero Health highlights the potential of virtual therapy through its secure, HIPAA-compliant video services. Their offerings include:
| Service Type | Features | Clinical Support |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Therapy | Same-week appointments; ages 5–95 | Licensed therapists |
| Medication Management | Virtual psychiatry consultations | Board-certified psychiatrists |
| Crisis Care | Urgent mental health support | Emergency response team |
Benefits of Online Therapy
Virtual therapy platforms, like those modeled by Televero Health, offer several advantages:
- Wider Access: Telehealth breaks down geographic barriers, which is critical for the 134 million Americans living in areas with a shortage of mental health professionals.
- Consistent Results: Studies confirm that VDP achieves outcomes similar to in-person therapy, with an effect size of +0.99 [95% CI: 0.67–0.31].
- Better Attendance: Holding sessions from home often leads to higher participation rates.
Therapy Costs and Coverage
Virtual therapy not only improves access but is often more affordable than traditional in-person sessions:
| Service Type | Average Cost | Insurance Copay Range |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Sessions | $100–$250 | $20–$60 |
| Online Platforms | $65–$95 | $0–$25 |
| Subscription Services | $50–$110/week | Varies by provider |
Many insurance providers now cover telehealth services. For example, Talkspace reports that over 100 million Americans have insurance coverage for online therapy, with some plans offering copays as low as $0.
“Often therapists will charge patients without insurance the same reimbursed rate they receive from insurance.”
- Virgie Bright Ellington, Internal Medicine Physician and Medical Billing Expert
Additionally, the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) requires insurance companies to treat mental health coverage the same as medical care, further supporting access to virtual therapy.
Conclusion
Research Summary
Studies show that therapy has a measurable impact on the brain. Brain imaging reveals that psychotherapy changes both brain structure and function, often delivering longer-lasting benefits than medication. Large-scale studies highlight therapy’s ability to lower disability rates, reduce mortality, and cut overall costs. For example, treated patients experienced a 17% reduction in costs, compared to a 12.3% increase for those who went untreated. Therapy also helps prevent relapse in conditions like anxiety and mild-to-moderate depression, with improvements lasting up to 5–6 years. Even for PTSD, progress can continue for up to two years after treatment.
“Every day, consumers are bombarded with ads that tout drugs as the answer to their problems. Our goal is to help consumers weigh those messages with research-based information about how psychotherapy can provide them with safe, effective and long-lasting improvements in their mental and physical health.” – Melba J. T. Vasquez, PhD, past president of the American Psychological Association
This evidence provides a solid foundation for making informed decisions about starting therapy.
Next Steps for Treatment
If you’re considering therapy, here are some practical steps to get started:
First, clarify your treatment goals. Therapy costs typically range from $100 to $200 per 50-minute session, though prices can vary. Virtual options, like Televero Health, make therapy more accessible, offering same-week appointments and accepting insurance. Aim to attend three to five sessions to see if the therapist is a good match for you.
Here’s a quick look at some evidence-based therapy options:
| Treatment Type | Best For | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| CBT | Anxiety, Depression | Improved brain connectivity and reduced symptoms |
| Combined Therapy | Severe Depression | Better overall functioning and quality of life |
| Preventive CT | Relapse Prevention | Delayed return of symptoms |
Therapy works best when you actively participate. Research shows that combining professional support with personal effort can lead to lasting changes in brain function and everyday well-being. Whether you choose in-person sessions or telehealth services, taking this step toward mental health care is a proven way to improve your life over the long term.
Related Blog Posts
- Does Therapy Really Work? Science-Backed Reasons to Give It Another Look
- Your Perfect Match: A Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the Therapist Who ‘Gets’ You
- No Struggle Too Small: How Therapy Helps Even When You Think You ‘Don’t Need It’
- Standing Your Ground: Overcoming Family or Social Pressure Against Therapy
